Knee replacement surgery: for your information
Routine surgery
Knee replacement surgery usually lasts 1-2 hours. This is a so called routine surgery, which may still somewhat vary depending on the exact patient.
Anaesthesia
Knee replacement surgery is performed while patient is asleep, so that he or she doesn't feel pain during the procedure. It’s described in medical terms as general anaesthesia.
The surgery is carried out under general as well as under local anaesthesia. General anaesthesia puts a patient in a sleep-like state, which turns off signal perception, that include pain signals and muscle tension. The patient doesn't remember anything about the surgery, as opposed to the procedure with local anesthetics, that keeps the patient conscious. The anaesthetic is delivered into a specific body part, causing its numbing. The patient doesn't feel anything on the surgical site, but is able to talk and answer questions.
Possible risks
Any type of anesthetic agent may cause complications that include, for example, circulatory system failure. However, severe complication are hardly to encounter nowadays. Before the surgery the patient has an appointment with an anesthesiologist, who will clarify the anaesthesia procedure and answer your questions. We recommend making a list of important questions prior to the appointment, in order not to forget them.
During the procedure
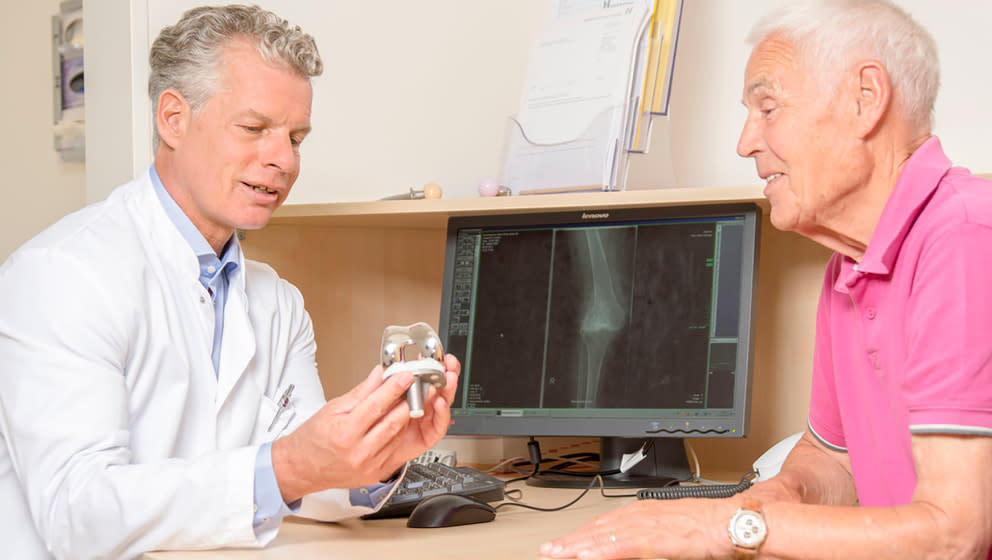
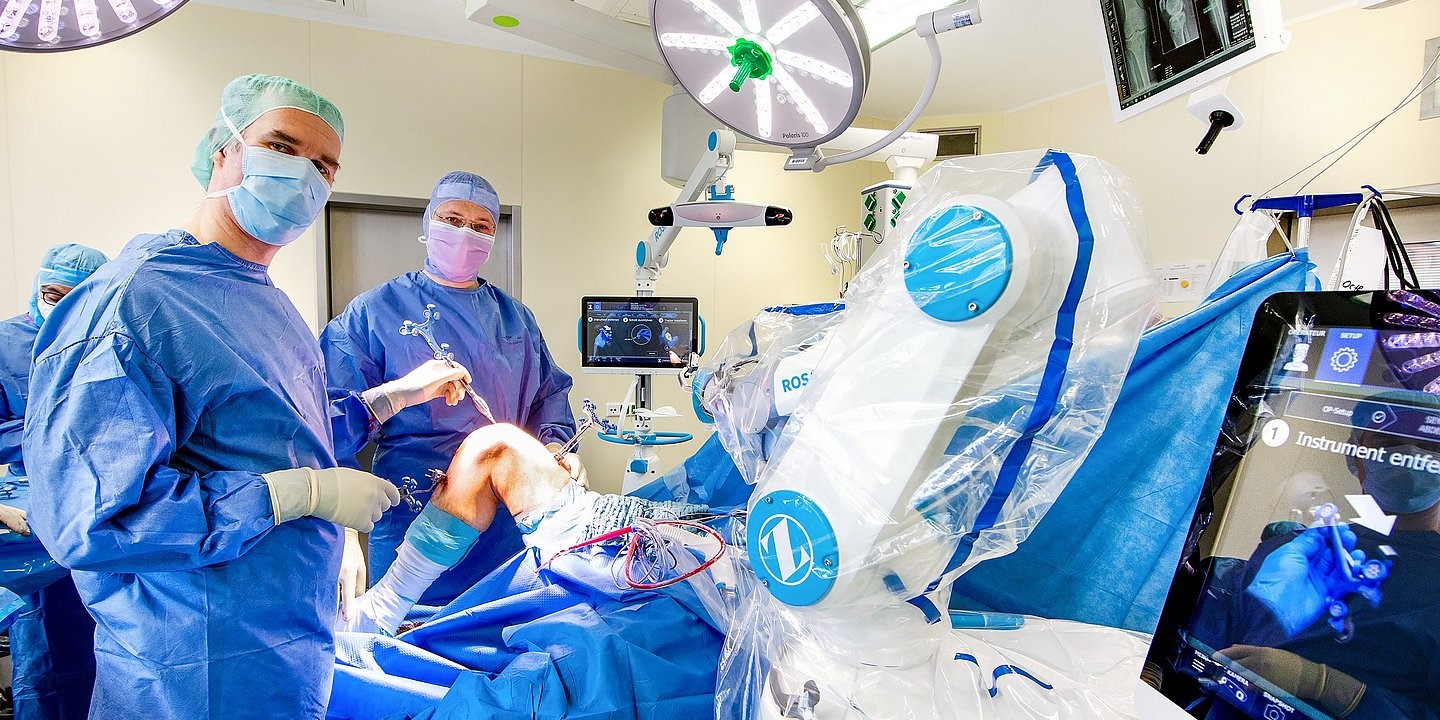
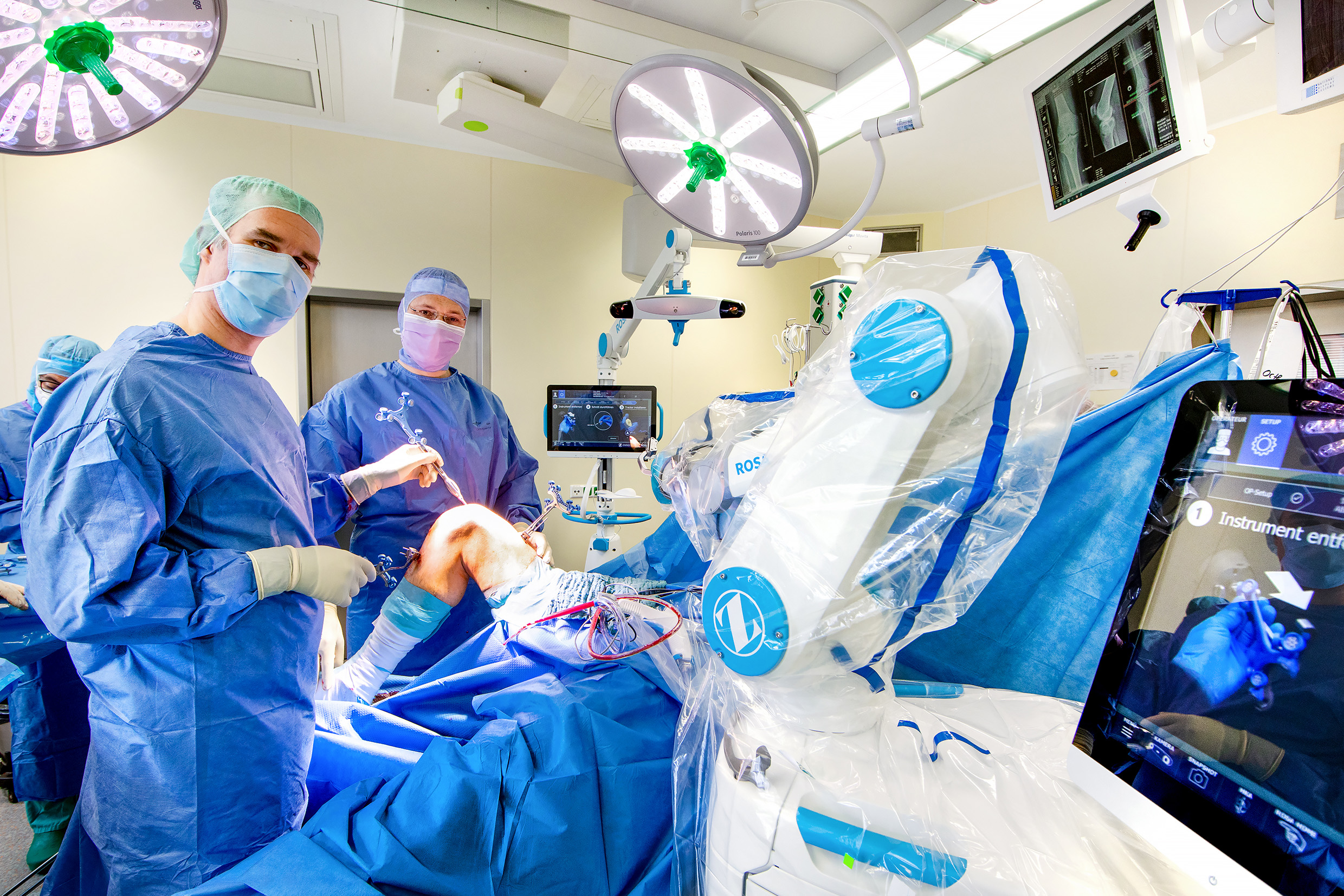
The surgeon needs only one incision to gain access to the knee joint and expose the knee. The surfaces of the joint are prepared carefully in order to attach the implant components precisely. The surgeons ensures prior to the implantation that the test implant is stable and bends correctly. If the implant works properly, the surgeon inserts a suitable implant and closes the incision.
In some cases, the surgeon might leave a special tube – drainage – that drains the blood from the wound, thus preventing the developing of a hematoma. However, it's not always necessary.
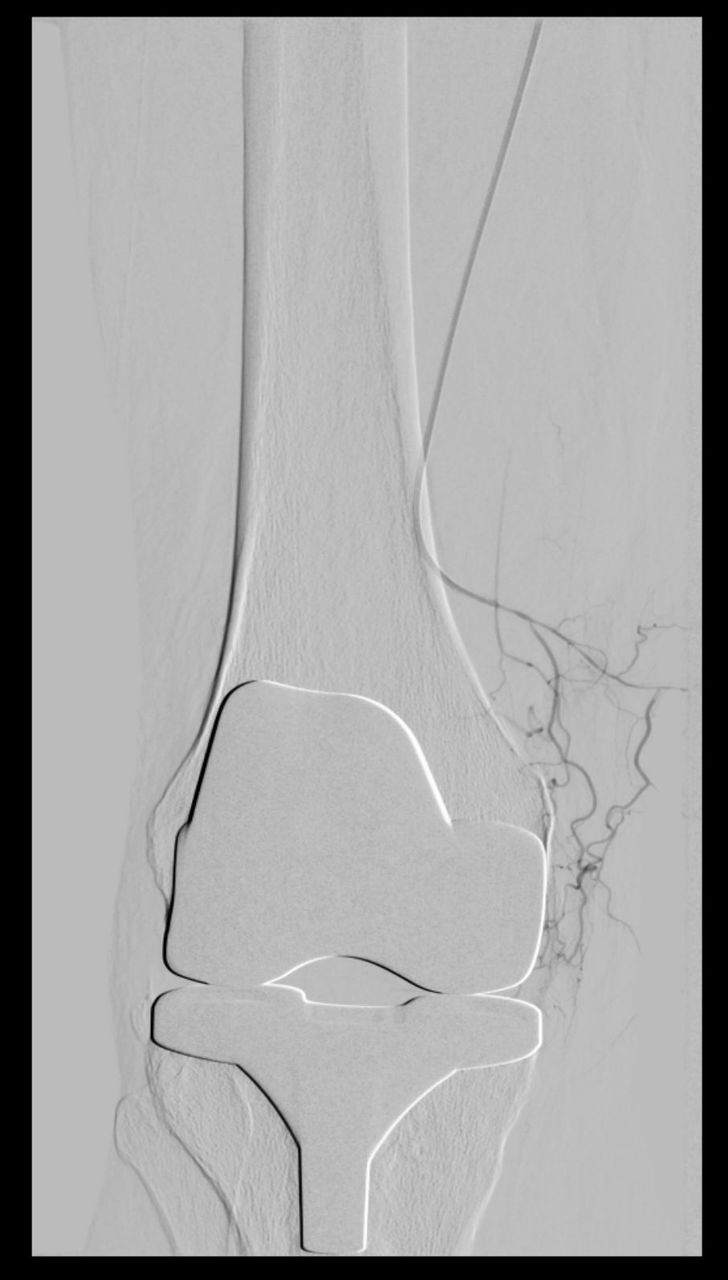
After the surgery, a knee x-ray is required, in order to check the implanted prosthesis. The patient is then accompanied by the anesthesiologist to the recovery room, where he or she will be treated before transferring to the hospital room.
Surgical techniques
The surgeon chooses a technique considering a type and a degree of the osteoarthrosis. A decision between partial or total knee replacements is made based on the extent of the joint damage.
Unicondylar prosthesis
A unicondylar prosthesis or sliding prosthesis is used to resurface only one damaged compartment of a knee.
Bicondylar prosthesis
If the surfaces of the both femur and tibia condyles are damaged, they are replaced with a bicondylar prosthesis with fixed or mobile bearing. The femur and tibia components of this prosthesis aren't connected with each other, so the ligaments, tendons and muscles alone have to restore the implant stabilization.
Constrained condylar knee prosthesis
A prosthesis with solid connection between the femur and the tibia is used, when ligaments and muscles can't stabilize an implant and it's impossible to reconstruct them.
Types of fixation
During the procedure the surgeon choses a type of implant fixation, which suits the patient best. Several cases require a special bone cement.
Cemented joint replacement
Prosthetic joint components are affixed to the prepared femur and tibia surfaces with a fast-drying polymer (bone cement). A full weight-bearing is allowed shortly after the surgery.
Cementless joint replacement
Prosthetic joint surfaces can be attached to the bones also without cement, if the bone tissue is satisfactory. In these cases, the surgeon uses a special implant with rough surface. Biological compatibility of the materials allows the bones to grow into the prosthesis that ensures a stable implant fixation.
Hybrid total knee arthroplasty
Hybrid total knee arthroplasty combines two methods of fixation - with cementless femoral and cemented tibial components.
Surgery wound
Once the procedure is done, the surgeon checks the wound for inflammation signs and applies a bandage using the latest techniques. If the surgeon inserted a drainage - a special tube that stays in the wound after the surgery and drains fluids such as secret or blood from the wound - it will be removed in a couple of days.
In order to protect the wound, a film dressing is applied. The patient is even allowed to take shower, but it should be discussed with medical personnel in advance.
The stitches are removed in 10-14 days. As soon as the wound is healed, the patient is allowed to start hydrokinesitherapy - rehabilitation physical therapy in a swimming pool.
NB: It's important to protect the scar from heat and sunlight during the first period after the discharge from the hospital. In case of scar redness, see a doctor.
Risks
Knee joint replacement is a routine surgery, which means that the complication are very rare. However, just like by any other surgery, there is always a risk of infection, onset of hematoma, thrombosis (vascular disease, which leads to blood clot, known as a thrombus) or embolism - partial or full blood vessel blockage.
All possible risk and information about postoperative rehabilitation are explained by the surgeon prior to the procedure.