Bypass operation
Bypass surgery
In order to restore the proper blood supply in the heart, damaged with narrowed coronary vessels, the doctors at Helios perform a special surgery.
Bypass surgery is used to treat narrowing of the coronary arteries when treatment with drugs or stents and a change in lifestyle don’t work anymore.
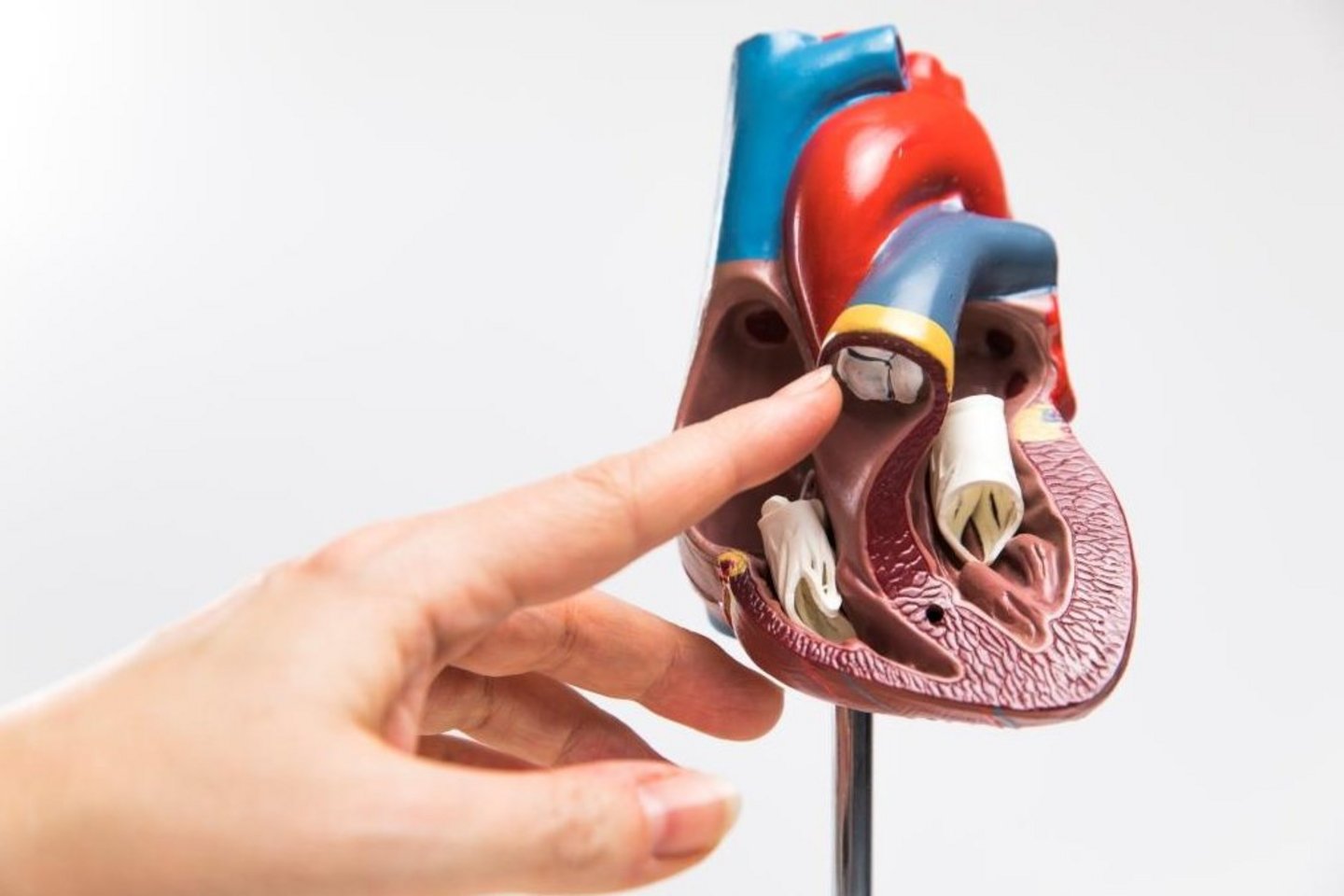
The coronary vessels derive from the aorta and supply the heart muscle with blood. Narrowing of the coronary arteries means that deposits in the coronary artery can no longer supply the heart muscle with sufficient blood. In a bypass operation, special bridges – a bypass – are made to avoid these narrowings. The doctors can take a new blood from different parts of the body and then sutures it to the aorta and the narrowed coronary vessel.
After various examinations and interviews with each patient, the surgeon decides individually which blood vessels and surgical method can be used for a bypass surgery. All Helios clinics employs only the latest and patient-friendly procedures.
How does a bypass operation work?
- On the admission day to the ward, doctors get a detailed information from you, check your documents and carry out any other necessary examinations, e.g. blood tests, X-rays, echocardiography. When all documents and examinations are complete, the surgeon and the anesthesiologist discuss a necessary surgery with you.
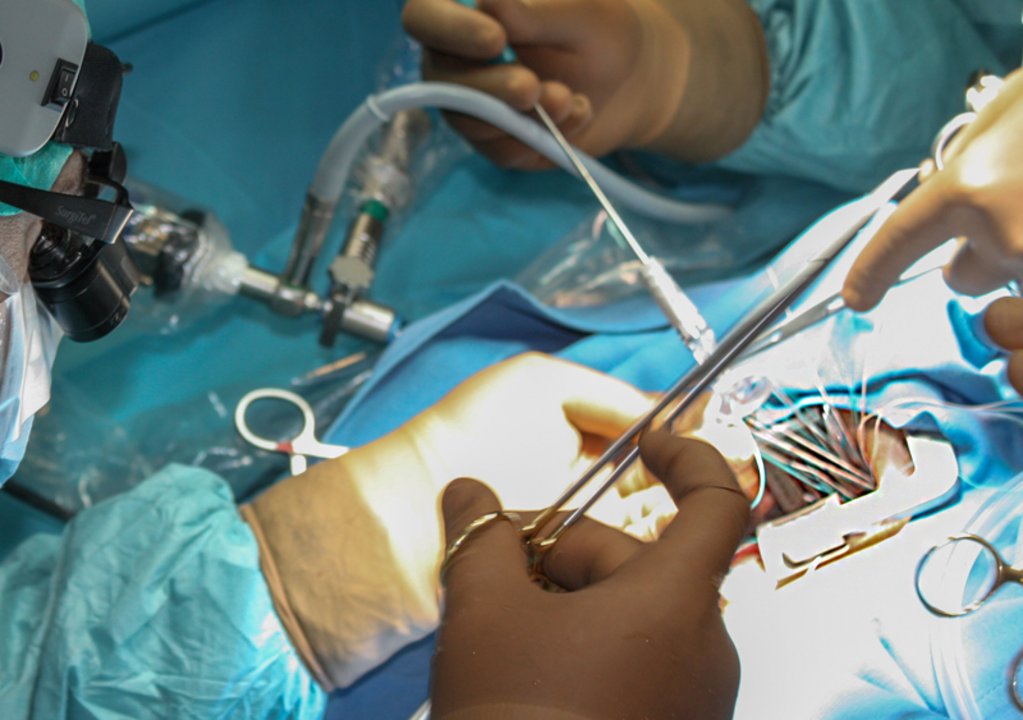
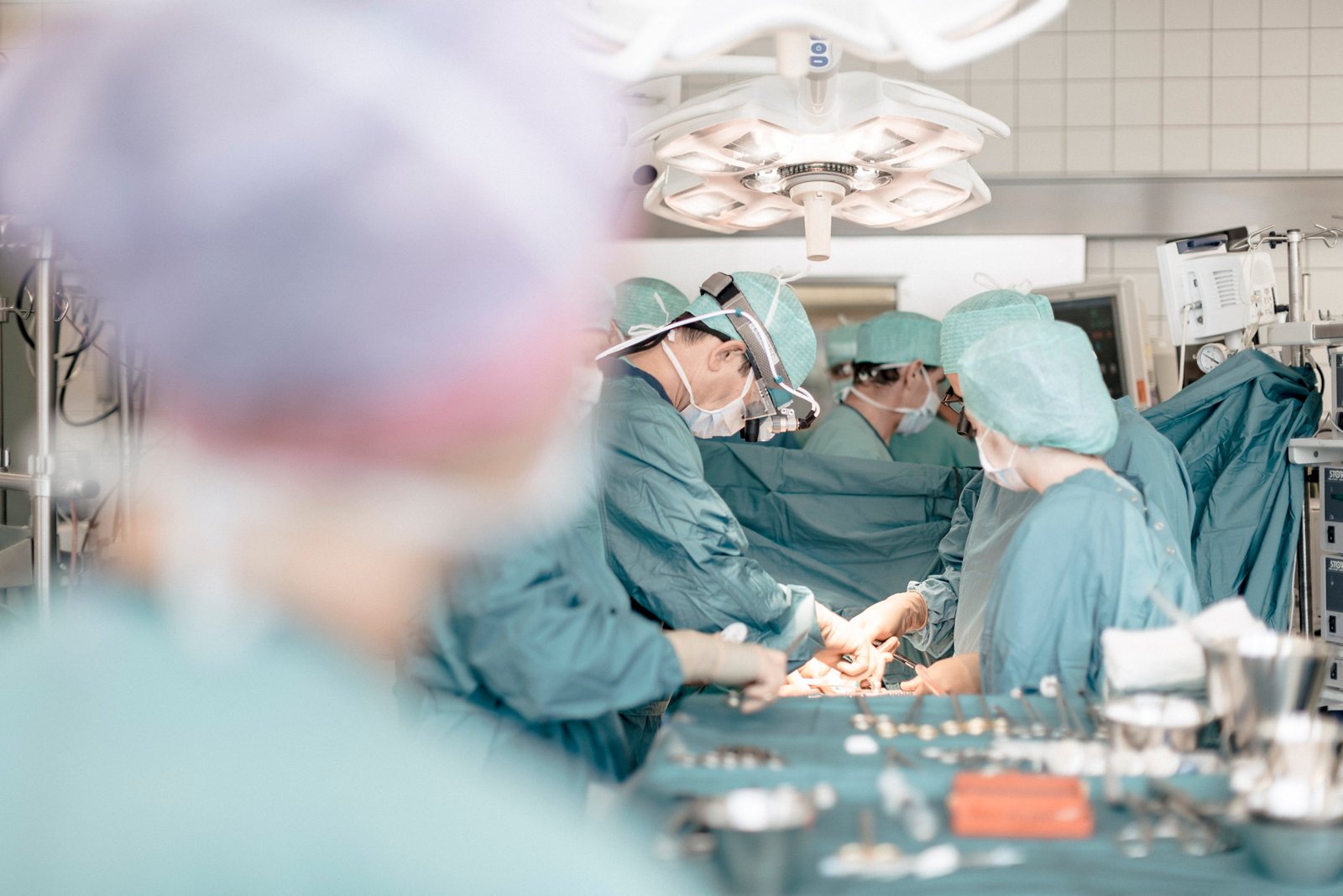
- The surgery takes place the following day. It’s performed under general anesthesia. At the beginning of the surgery, the doctors open the chest and remove the bypass vessels from the chest wall, arm or lower leg, depending on the number required. Then, if necessary, you’ll be connected to the heart-lung machine and the heart is stilled. The bypass vessels are connected to the aorta and the damaged coronary arteries. Then the heart-lung machine is removed and the sternum and an incision are carefully sealed.
- During the next 24 hours you’ll be monitored in one of our monitoring stations (Intermediate Care).
- Then you’ll be transferred to a normal ward. The length of stay is normally seven days.
Which patient-friendly surgical methods are available?
Modern bypass surgery offers various patient-friendly surgical methods. They reduce the risk of complications, such as impaired wound healing or stroke. You’ll also recover faster and won’t have to stay in a hospital for a long time. The doctors ensure every single time, that the condition of a patient allows such surgery.
Off-pump coronary artery bypass (OPCAB)
A bypass operation can be performed on the beating heart without using the heart-lung machine, depending on the patient’s condition. In this case, the operating area is fixed by a stabilizer, which supports the function of the other parts of the heart, thus allowing a safe procedure.
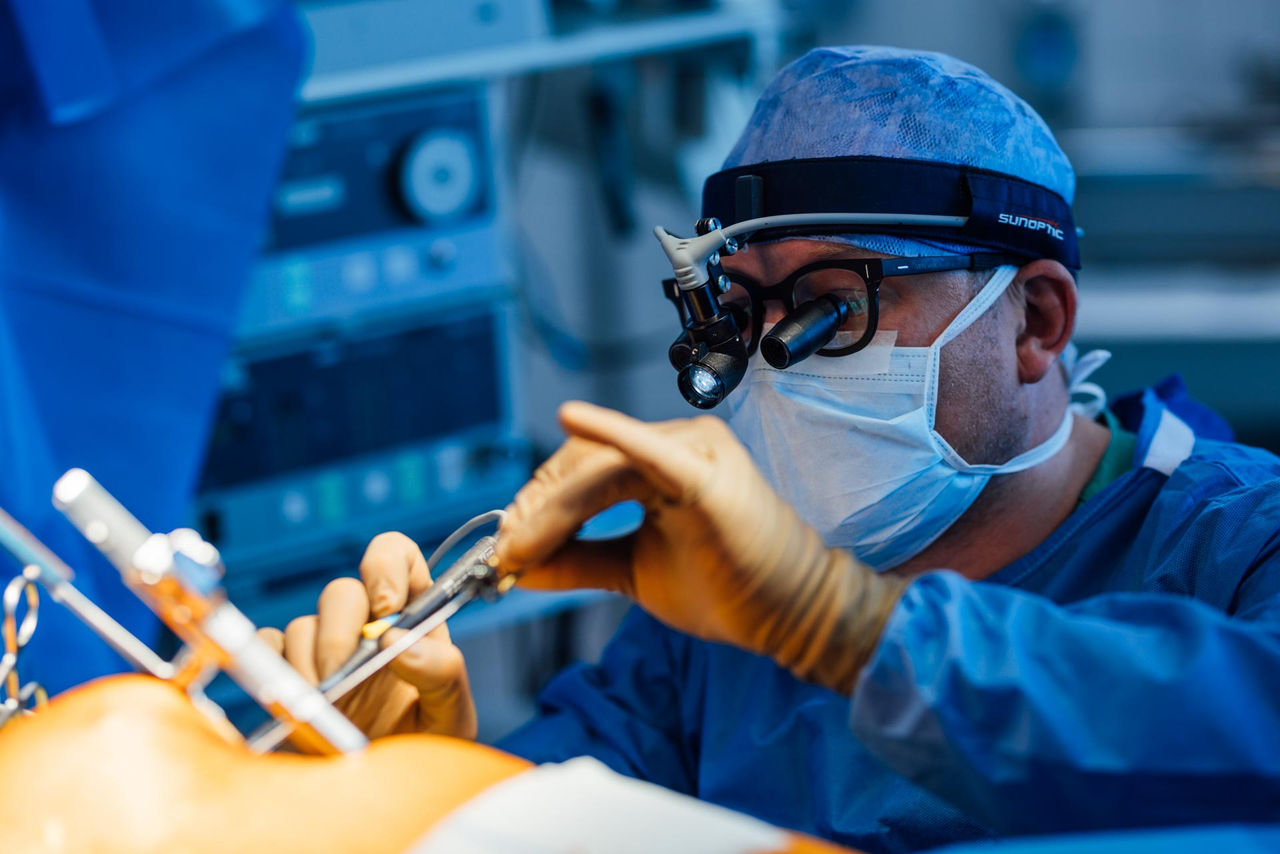
Minimally invasive bypass surgery (MIDCAB, MV-MIDCAB)
A bypass surgery can also be performed with a closed chest, especially if the narroed blood vessels are located on the front or side wall of the heart. In this case, the procedure is performed through a small incision in the left or right chest wall. This surgical technique can also be performed on the beating heart.
The University Hospital for Cardiac Surgery has one of the world's greatest experiences in the field of minimally invasive bypass surgery.
Minimally invasive blood vessel removal
If the blood vessels need to be removed from the forearm (arteries) or leg (veins), this is done through a small incision with video-assisted technology (endoscopic removal). This reduces the risk of wound infections and improves the healing process.
How safe is a bypass operation?
Bypass surgery is the most frequently performed heart surgery at the Heart Center Leipzig and is one of the safest surgical procedures in heart surgery.
The surgical risk is determined by the age, physical condition, the presence of concomitant diseases and the urgency of the bypass surgery (emergency or planned surgery).
Your surgeon discusses all risks with you individually during a consultation.
Bypass operation outcome
Bypass surgery helps to restore blood flow to the heart muscle, reduce the symptoms of coronary artery disease such as shortness of breath, chest pain, fatigue and cardiac arrhythmia, and prolong your life.